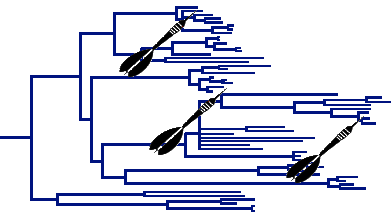
Phylogenetic targeting
 References:
References:
Arnold, C., Nunn, C. L. 2010. Phylogenetic Targeting of Research Effort in Evolutionary Biology. American Naturalist 176:601-612. [PDF]
Project Description:
Here, I will introduce one of my previous research projects,
Phylogenetic Targeting, which is more fully described in the official publication and in my
Master's thesis [pdf]. For more information and a web
implementation of the program, see http://phylotargeting.fas.harvard.edu. In what follows, we provide an abstract of the project.
Many questions in comparative biology require that
new data be collected, either to build a comparative database for the
first time or to augment existing data. Given resource limitations in
collecting data, which species should be studied to increase the size of
comparative data sets? By taking the hypotheses, other comparative data
relevant to the hypotheses, and an estimate of phylogeny, we show that a
method of phylogenetic targeting can systematically identify the
species that offer the greatest statistical power to test the
hypotheses. Phylogenetic targeting selects potential candidates for
future data collection based on a flexible scoring system that maximizes
the differences in pairwise comparisons. The method can control for
confounding variables, or it can maximize the power to test competing
hypotheses. We used simulations to assess the performance of
phylogenetic targeting, as compared to a less systematic approach of
randomly selecting species (as might occur when data have been collected
on species without regard to variation in the traits of interest). The
simulations revealed that selection of species using phylogenetic
targeting increases the statistical power to detect correlations and
that power increases with the number of species in the clade even when
the number of samples collected was not increased. We also developed a
web-based, freely available and publicly accessible computer program
PhyloTargeting that implements the approach. It provides a
user-friendly interface, a variety of options to analyze the data set,
and graphical visualizations of the results.